Open Authentication (OAuth2)
Introduction
OAuth2 (OpenAuthentication) is summarized in RFC 6749 as follows:
The OAuth 2.0 authorization framework enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to an HTTP service, either on behalf of a resource owner by orchestrating an approval interaction between the resource owner and the HTTP service, or by allowing the third-party application to obtain access on its own behalf.
Here is an overview of how the process works:
The OAuth2 App
OAuth2 support is available in ownCloud via the OAuth2 application which is available from the ownCloud Marketplace. The app aims to:
-
Connect ownCloud clients (both desktop and mobile) in a standardized and secure way.
-
Make 3rd party software integrations easier by providing an unified authorization interface.
Requirements
To use the OAuth2 app, your ownCloud installation will need to meet the following dependencies:
-
Apache: If you are hosting your ownCloud installation using the Apache web server, then mod_rewrite and mod_headers modules must be installed and enabled.
-
Redis: You will need to have a Redis server available, ideally the latest, stable version.
-
PHP-Redis: You PHP installation must have the php-redis extension (>= 4.2) installed and enabled.
See the Detailed Installation Guide for how to install Redis and PHP-Redis.
Installation
To install the application, download the OAuth2 app from the marketplace to the ownCloud app directory or use the Market app.
Basic Configuration
To enable token-only based app or client logins in config/config.php, set token_auth_enforced to true. This prevents new clients logging in via username and password. Existing client connections remain active, until they log out. See config sample file for more details.
The OAuth2 app comes with a set of occ commands to configure clients. For more information on usage of occ for OAuth2, see section OAuth2 Commands.
|
Trusting Clients
Since version 0.5.0 of the OAuth2 app, you can mark clients as trusted. This will have the effect that the consent step in the authentication process will be skipped for this client.
Only mark trustworthy clients and web apps under your control as trusted. Apps which cannot keep the Client Identifier (ID) secret or have redirect URIs which can not be fully controlled should not be marked as trusted.Refer to the official OAuth2 RFC sections 10.1 and 10.2 for further information about the risks. |
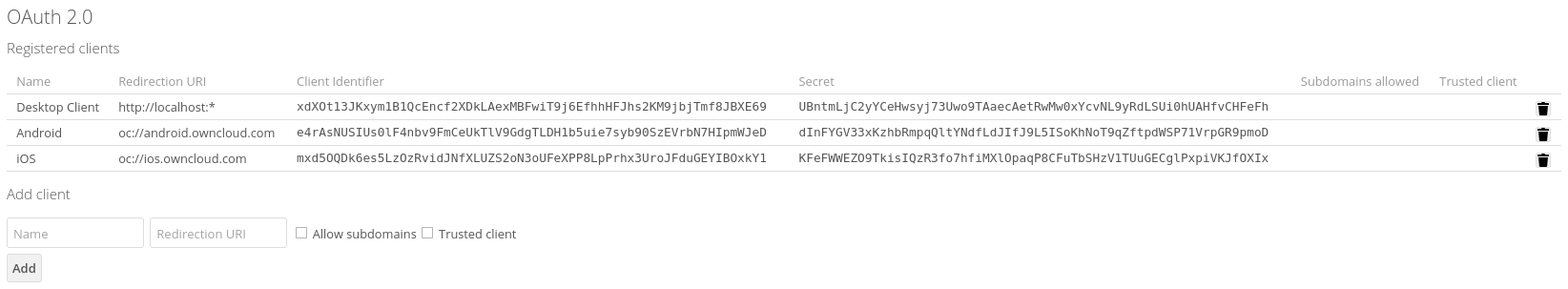
If you want to mark an existing client as trusted, you have to:
-
Copy the
Client Identifier (ID)and theClient Secret. -
Then delete the existing entry either in the UI or via the occ oauth2 remove command.
-
And finally add it again with the occ oauth2 add command with the trusted setting enabled.
When deleting in the web UI, you might need to scroll horizontally to see the delete buttons. Follow this link regarding Client IDs, Secrets and Redirect URIs for ownCloud clients.
Protocol Flow
Client Registration
Clients first have to be registered in the web-UI . You need to specify a name for the client (the name is unrelated to the OAuth 2.0 protocol and is just used to recognize it later) and the redirection URI. A client identifier and client secret are generated when adding a new client, which both consist of 64 characters.
Refer to the official client registration RFC from the IETF for further information about client registration.
Authorization Request
For every registered client, an authorization request can be made. The client redirects the resource owner to the authorization URL and requests authorization. The following URL parameters have to be specified:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
yes |
Needs to be |
|
yes |
The client identifier obtained when registering the client. |
|
yes |
The redirection URI specified when registering the client. |
|
no |
Can be set by the client "to maintain state between the request and callback". See `RFC 6749`_ for more information. |
Refer to the official authorization request RFC from the IETF for further information about client registration.
Authorization Response
After the resource owner’s authorization, the app redirects to the redirect_uri specified in the authorization request and adds the authorization code as URL parameter code. An authorization code is valid for 10 minutes.
Refer to the official authorization response RFC from the IETF for further information about client registration.
Access Token Request
With the authorization code, the client can request an access token using the access token URL. Client authentication is done using basic authentication with the client identifier as username and the client secret as a password. The following URL parameters have to be specified:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Use either |
|
|
If the grant type |
|
|
If the grant type |
|
|
If the grant type |
Refer to the official access token request RFC from the IETF for further information about client registration.
Access Token Response
The app responds to a valid access token request with a JSON response like the following. An access token is valid for 1 hour and can be refreshed with a refresh token.
{
"access_token" : "1vtnuo1NkIsbndAjVnhl7y0wJha59JyaAiFIVQDvcBY2uvKmj5EPBEhss0pauzdQ",
"token_type" : "Bearer",
"expires_in" : 3600,
"refresh_token" : "7y0wJuvKmj5E1vjVnhlPBEhha59JyaAiFIVQDvcBY2ss0pauzdQtnuo1NkIsbndA",
"user_id" : "admin",
"message_url" : "https://www.example.org/owncloud/index.php/apps/oauth2/authorization-successful"
}Refer to the official access token response RFC from the IETF for further information about client registration.
| For a succinct explanation of the differences between access tokens and authorization codes, check out this answer on StackOverflow. |
Limitations
-
Since the app does not handle user passwords, only master key encryption works (similar to the Shibboleth app).
-
Clients cannot migrate accounts from Basic Authorization to OAuth2, if they are currently using the
user_ldapbackend. -
It is not possible to explicitly end user sessions when using OAuth2. Have a read through User Authentication with OAuth 2.0 to find out more.